Pakistan-Linked Cyber Campaigns Target Indian Government Using Google Sheets & Fake Adobe Updates
Indian government entities have been targeted by two sophisticated cyber-espionage campaigns, dubbed Gopher Strike and Sheet Attack, attributed to a Pakistan-linked threat actor. The attacks leverage phishing emails, fake Adobe update prompts, and trusted platforms like Google Sheets and GitHub to deploy custom Golang-based malware, enabling persistent access and remote command execution on infected systems.

Indian government organizations have recently become targets of sophisticated cyber-espionage campaigns believed to be linked to a Pakistan-based threat actor. Security researchers at Zscaler ThreatLabz identified two distinct attack operations, named Gopher Strike and Sheet Attack, which use previously undocumented techniques and malware to compromise systems and maintain long-term access.
The Sheet Attack campaign abuses trusted cloud services such as Google Sheets, Firebase, and email platforms to establish command-and-control (C2) communication. By leveraging legitimate services, attackers successfully evade traditional security detection mechanisms while remotely issuing commands and exfiltrating data.
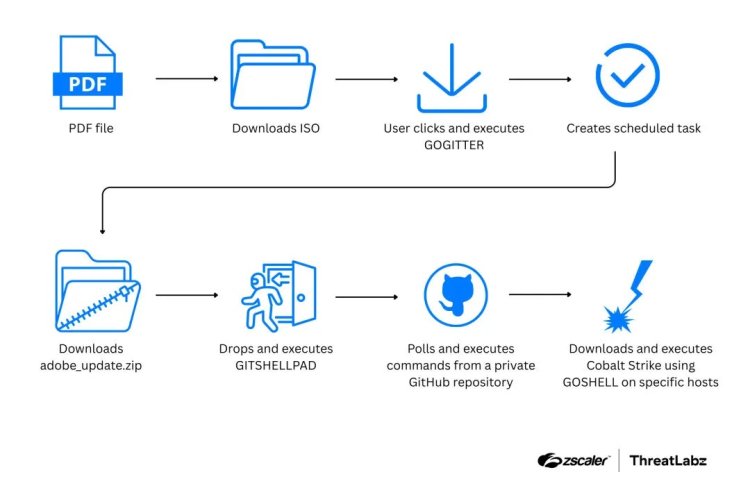
The Gopher Strike campaign begins with carefully crafted phishing emails containing malicious PDF documents. These PDFs display a blurred document with a fake pop-up prompting users to install an “Adobe Acrobat Reader update.” When victims click the download button, a malicious ISO file is delivered only to targets located in India and using Windows systems, helping attackers avoid automated analysis tools.
Once executed, the malware deploys Golang-based components such as GOGITTER, GITSHELLPAD, and GOSHELL, enabling persistence, remote command execution, and payload delivery. The attackers further abuse private GitHub repositories as part of their command-and-control infrastructure, blending malicious activity with normal developer traffic.
These campaigns highlight a growing trend in cyber warfare and espionage, where threat actors increasingly rely on trusted platforms and advanced evasion techniques to infiltrate high-value government targets. Organizations are advised to strengthen email security, monitor abnormal cloud service usage, and educate users about phishing and fake software updates to reduce exposure to such threats.